Formidable Accounting For Cash Pooling Arrangements
It may pose a liquidity risk at the sub-account level.
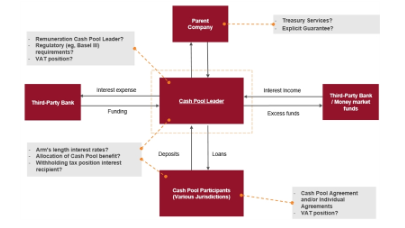
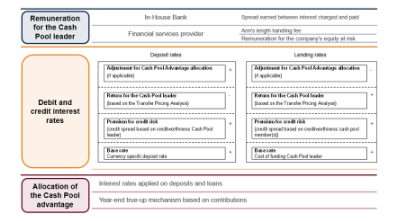
Accounting for cash pooling arrangements. Notional cash pooling and physical cash pooling. The cash pooling or cashpooling is a centralized cash management strategy to balance the accounts of a groups subsidiaries. The appropriate reward of the cash pool leader will depend on the functions performed the assets used and the risks assumed in facilitating a cash pooling arrangement.
There are two main types of cash pooling arrangements. The greatest advantage of pooling your cash together into a single cash pool is that you increase visibility and control over all your cash in different entities all around the world. Securities and loans held for dealing or trading.
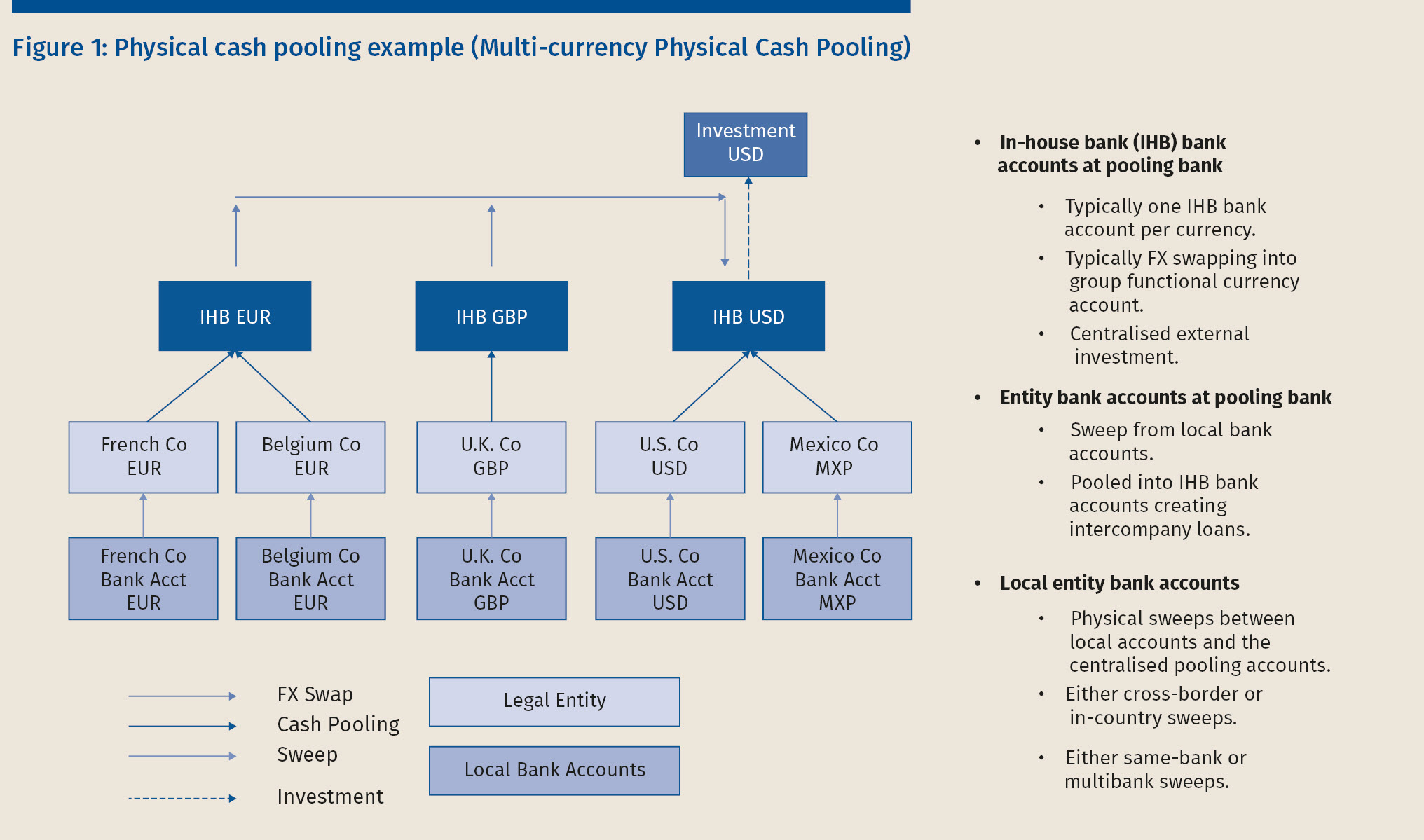
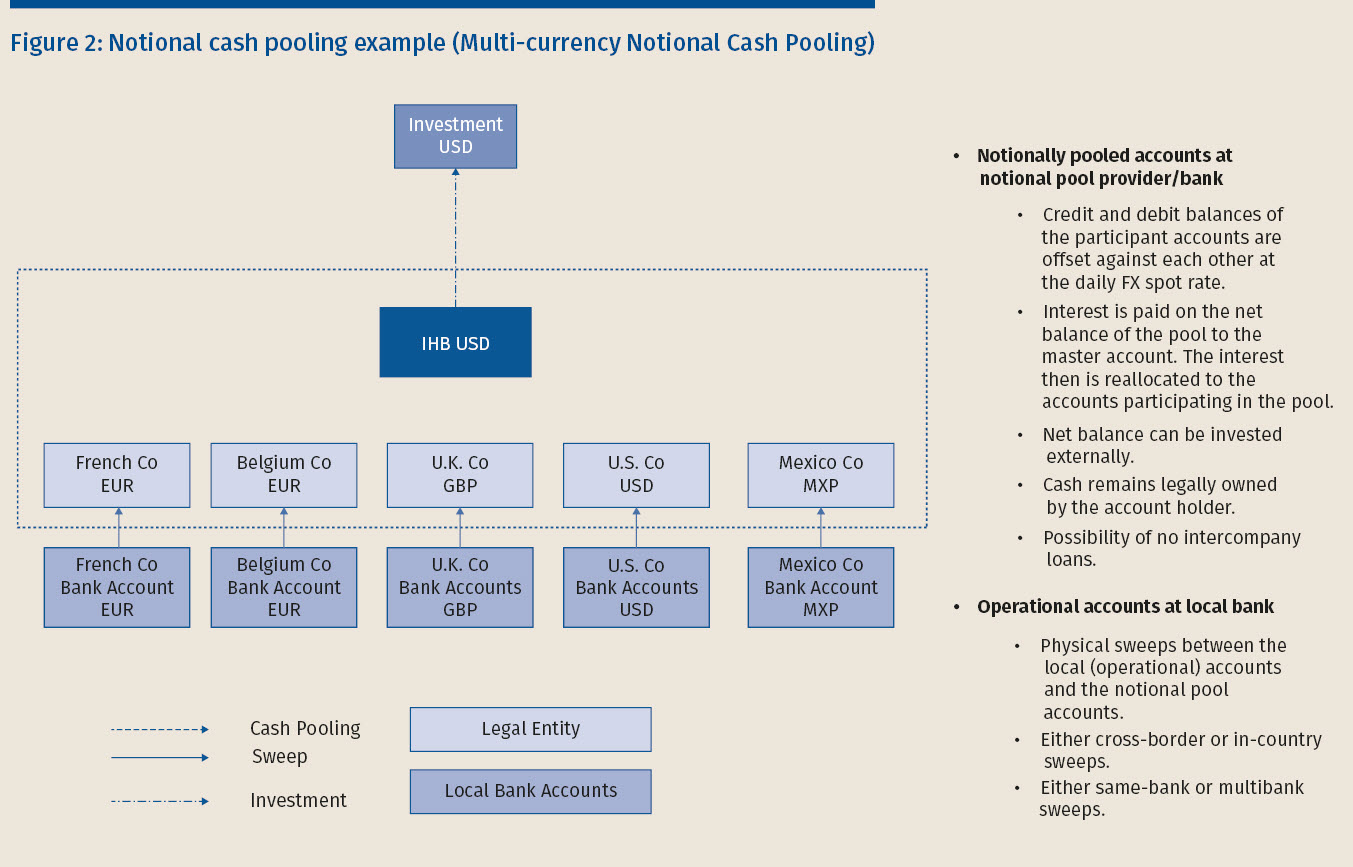
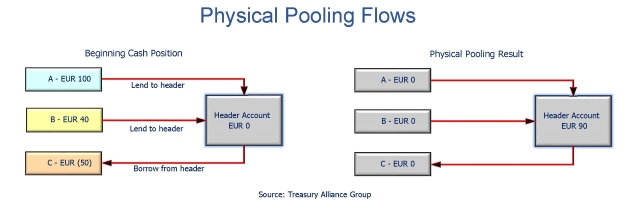
Arrangements are in line with their cash management strategy. Notional Cash Pool A notional cash pool allows the multinational group to net off the balances of various bank accounts across jurisdictions. Depending on a surplus or lack of cash all cash balances in the Pool Pool- Participants will be transferred on daily basis automatic to or from the top-mother account Pool-Leader.
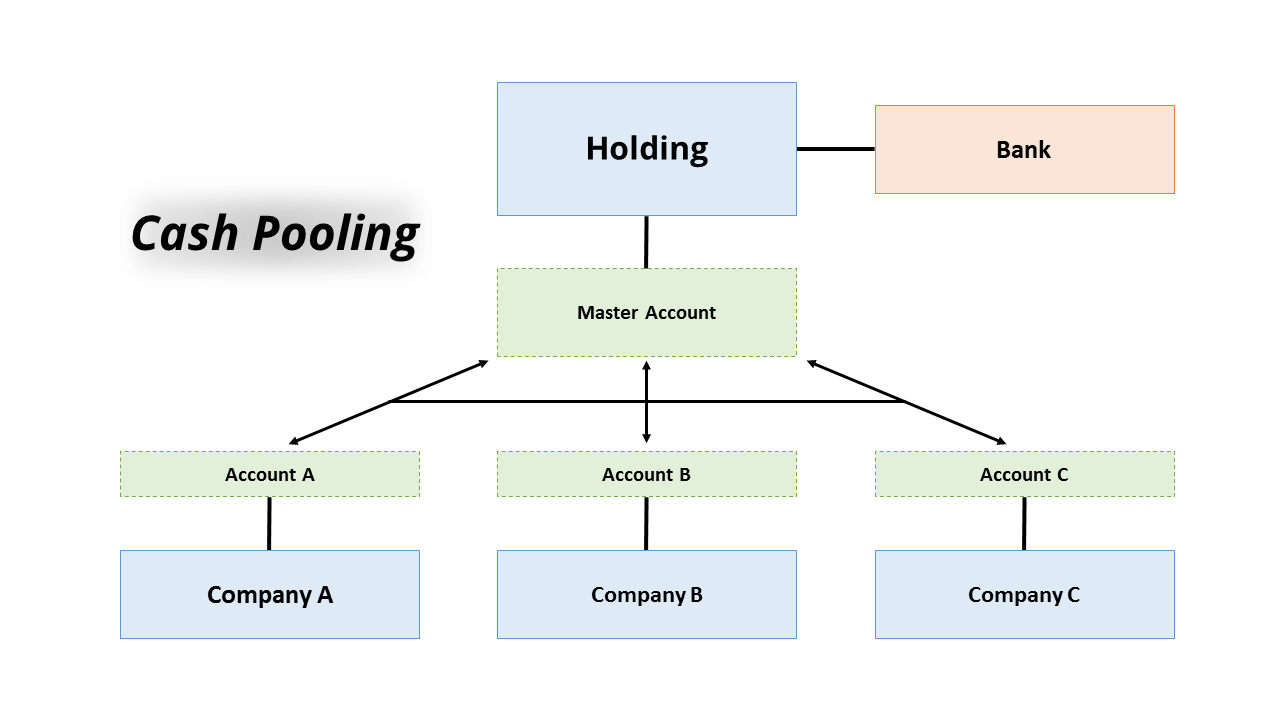
Group cash pooling and company accounts Cash pooling arrangements arise where one group entity which may be the ultimate group parent or a fellow subsidiary acts as the treasury function for the rest of the group. Under a cash pooling arrangement entities within a corporate group regularly transfer their surplus cash to a single bank account the master account and in return may draw on the funds in that account to satisfy their own cash flow requirements from time to time. Cash pooling arrangements.
Companies typically use a number of current accounts and cash-pooling gives them the opportunity to consolidate these bank accounts into a master account and accrue interest on a daily basis as a whole. Cash pooling is a liquidity management technique whereby funds are physically concentrated or notionally consolidated into a single cash position. Cash-pooling is an instrument used to optimise corporate accounts.
Improving the interest charge. It helps in centralized cash management for quick pooling and disbursement of funds. The IFRS Interpretations Committee has received a request to clarify whether certain cash pooling arrangements between subsidiaries in a group would meet the requirements for offsetting in IAS 32.