Outstanding High Current Ratio Interpretation
/DEBTEQUITYFINALJPEG-098e44fb157a41cf827e1637b4866845.jpg)
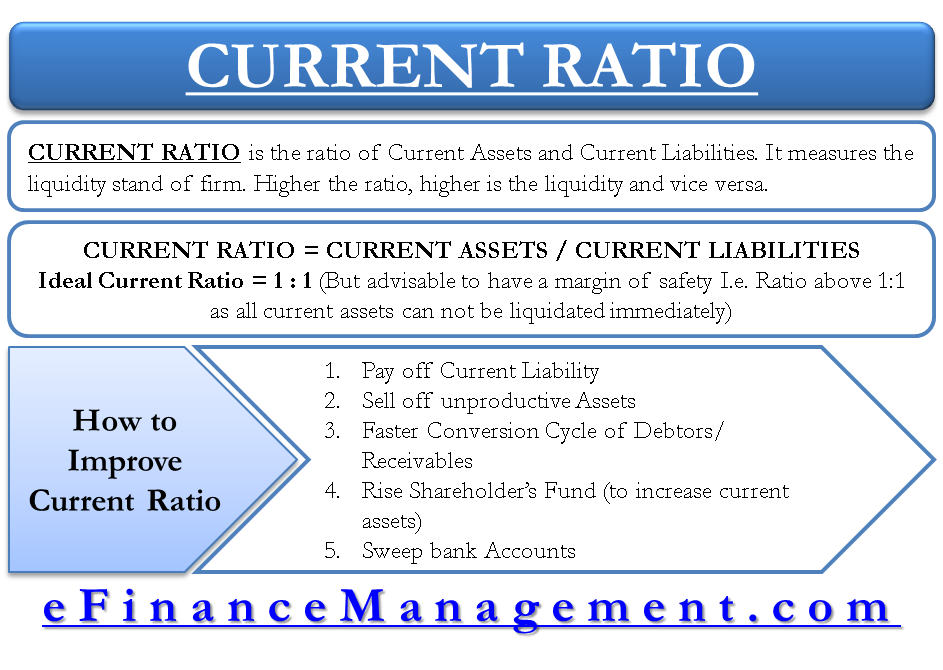
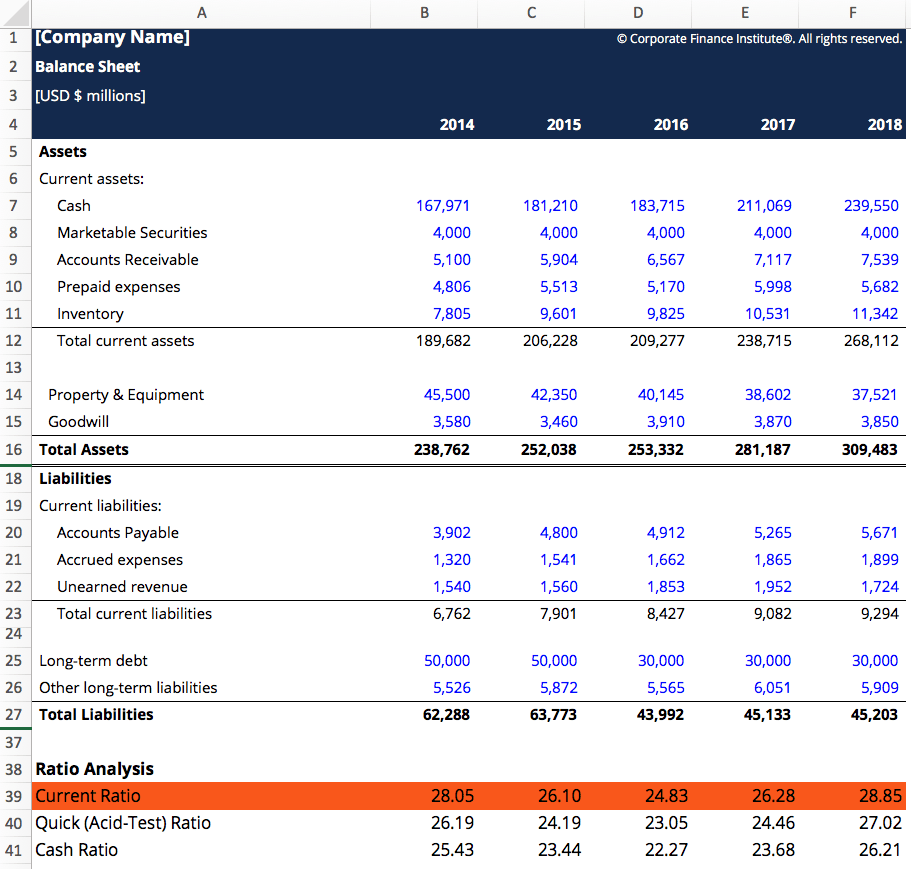
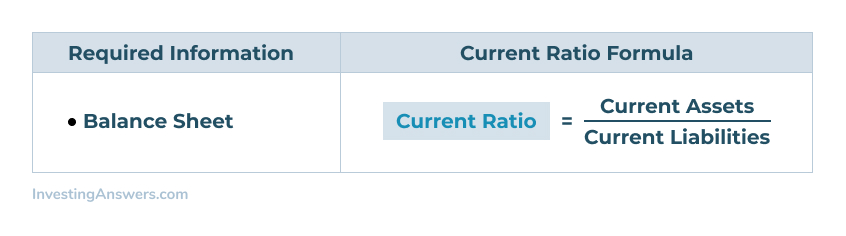
As a bankers rule of thumb the standard for current ratio is 21.
High current ratio interpretation. More cash balances are kept idle in banks. The amounts collected from debtors is not satisfactory. A current ratio of less than 1 could be an indicator the company will be unable to pay its current liabilities.
It is important to note that both of these are current. The higher the current ratio is the more capable the company is to pay its obligations. Increases in the current ratio over time may indicate a company is growing into its capacity while a decreasing ratio may indicate the opposite.
Generally a business with a current ratio under 1 is considered bad. This means that the assets and the liabilities are supposed to be met in the short run. Current ratio is also affected by seasonality.
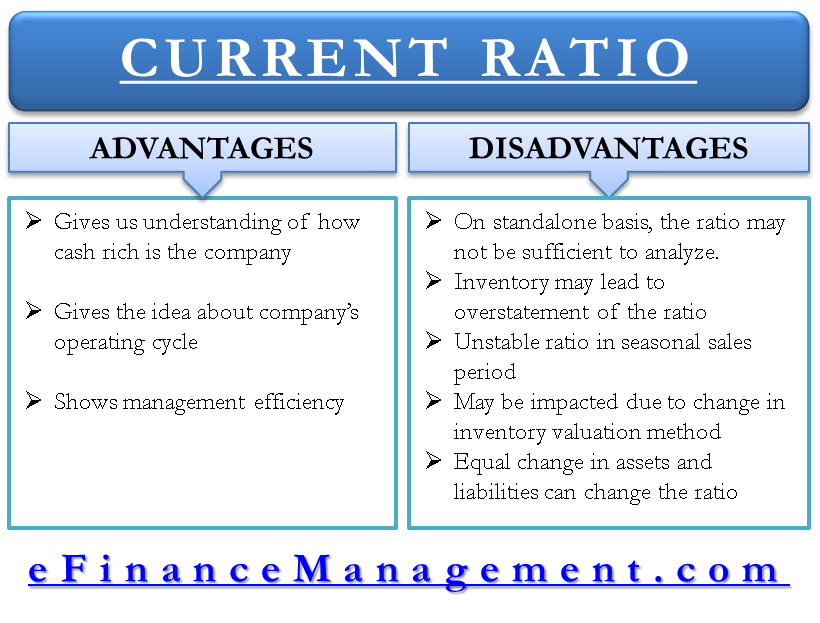
Reasons of Low Current Ratio. However a current ratio that is too high might indicate that the company is missing out on more rewarding opportunities. Hence companies with good quick ratios are favored by creditors.
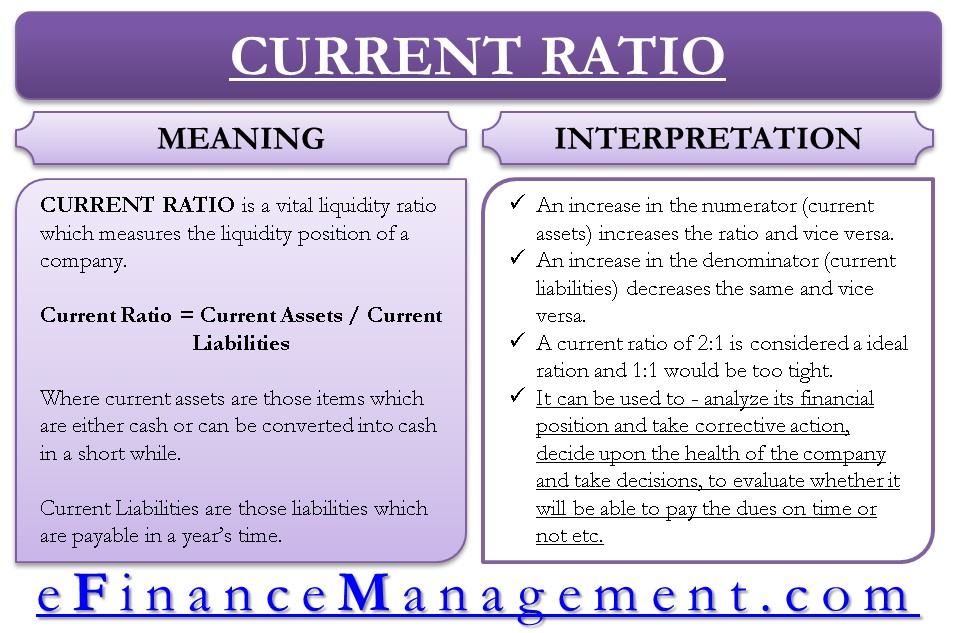
Theoretically a high current ratio is a sign that the company is sufficiently liquid and can easily pay off its current liabilities using its current assets. Investors typically look for a current ratio greater than 1 150 or even 2. It indicates whether the business can pay debts due within one year out of the current assets.
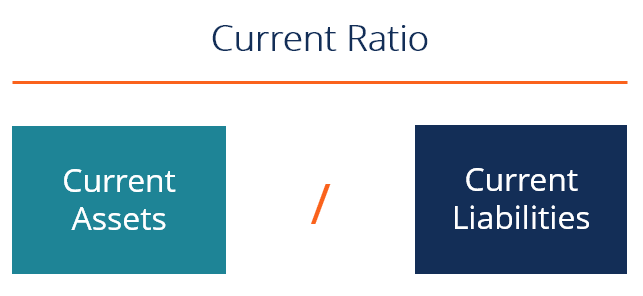
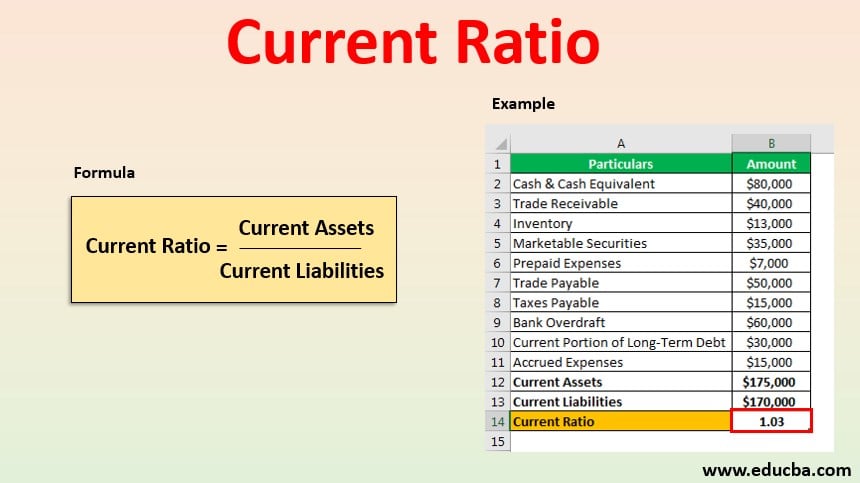
Current ratio is computed by dividing total current assets by total current liabilities of the business. A very high current ratio may indicate existence of idle or underutilized resources in the company. For example in the retail industry a store might stock up on merchandise.